Concrete grades are classified based on their compressive strength, which is measured in megapascals (MPa) after 28 days of curing. The grades range from M5 to M30 and beyond, each serving different structural requirements. Here’s a detailed look at the concrete grades from M5 to M30:
Concrete Grades: M5 to M30
1. M5 Grade Concrete
- Compressive Strength: 5 MPa
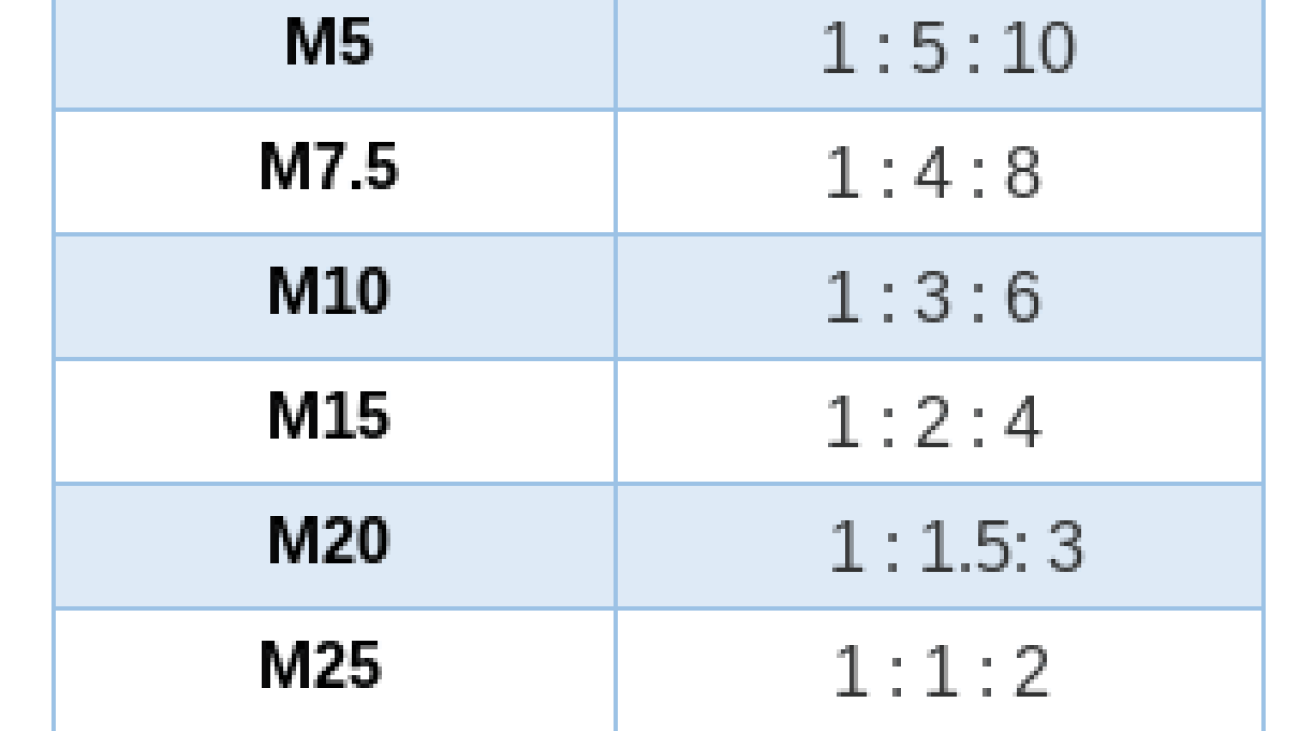
- Mix Ratio: 1:5:10 (Cement: Sand: Aggregates)
- Usage: Used for non-structural elements like leveling course, bedding for footings, and simple pathways.
2. M7.5 Grade Concrete
- Compressive Strength: 7.5 MPa
- Mix Ratio: 1:4:8
- Usage: Ideal for simple construction like driveways, walkways, and for levelling.
3. M10 Grade Concrete
- Compressive Strength: 10 MPa
- Mix Ratio: 1:3:6
- Usage: Used for non-structural elements, foundations of small buildings, and for blinding purposes.
4. M15 Grade Concrete
- Compressive Strength: 15 MPa
- Mix Ratio: 1:2:4
- Usage: Suitable for plain concrete work and flooring. It is often used in footpaths and simple slabs.
5. M20 Grade Concrete
- Compressive Strength: 20 MPa
- Mix Ratio: 1:1.5:3
- Usage: Commonly used in reinforced concrete construction for slabs, beams, columns, and footings. It’s the minimum grade of concrete recommended for RCC works.
6. M25 Grade Concrete
- Compressive Strength: 25 MPa
- Mix Ratio: 1:1:2
- Usage: Suitable for RCC works for structures like residential buildings, bridges, and commercial buildings. It offers higher strength than M20.
7. M30 Grade Concrete
- Compressive Strength: 30 MPa
- Mix Ratio: Design mix (proportions determined by the requirements of the specific construction project)
- Usage: Ideal for RCC works in high-strength structures such as heavy-duty industrial floors, commercial buildings, and high-rise residential buildings.
Detailed Considerations
- Compressive Strength Testing:
- Concrete strength is tested using cube or cylinder samples, cured for 28 days and subjected to compressive forces until they fail.
- Strength is measured in megapascals (MPa), which indicates the load-carrying capacity per unit area.
- Mix Design:
- For lower grades (M5 to M20), nominal mix ratios are used. These are predefined ratios of cement, sand, and aggregates.
- For higher grades (M25 and above), a design mix is used. The proportions of the components are determined based on the specific requirements of the project and are designed to achieve the desired strength and durability.
- Applications:
- Low Grades (M5 to M15): Typically used for non-structural elements and in applications where high strength is not crucial.
- Medium Grades (M20 and M25): Widely used in general RCC works for residential and commercial buildings.
- High Grades (M30 and above): Employed in structures that require high strength and durability, such as multi-story buildings, bridges, and heavy-duty industrial floors.
- Durability and Workability:
- As the grade increases, the concrete mix typically becomes denser and stronger, improving its durability and resistance to environmental factors.
- Higher-grade concrete often requires additives or admixtures to enhance workability and performance.
- Environmental Factors:
- Higher grades of concrete are often necessary in environments with extreme weather conditions, high loads, or aggressive chemical exposure.
Conclusion
Understanding the different grades of concrete from M5 to M30 is crucial for selecting the appropriate type for various construction needs. Lower grades are suitable for simpler, non-load-bearing applications, while higher grades are essential for structural elements that require significant strength and durability. Each grade serves a specific purpose, ensuring the safety, stability, and longevity of the constructed structures.

[…] Storey: Minimum column size is 9” x 9” (230 mm x 230 mm) using M20 grade concrete. However, this can vary based on the load and structural […]