Type D Soil
Designing columns for buildings, whether single-storey or multi-storey (up to 10 storeys), involves a comprehensive understanding of load distribution, material strengths, and soil conditions. Below are some thumb rules for column design and steel calculation for buildings up to 10 storeys, considering Type D soil (which generally indicates stiff soil or soft rock with moderate strength):
Thumb Rules for Column Design
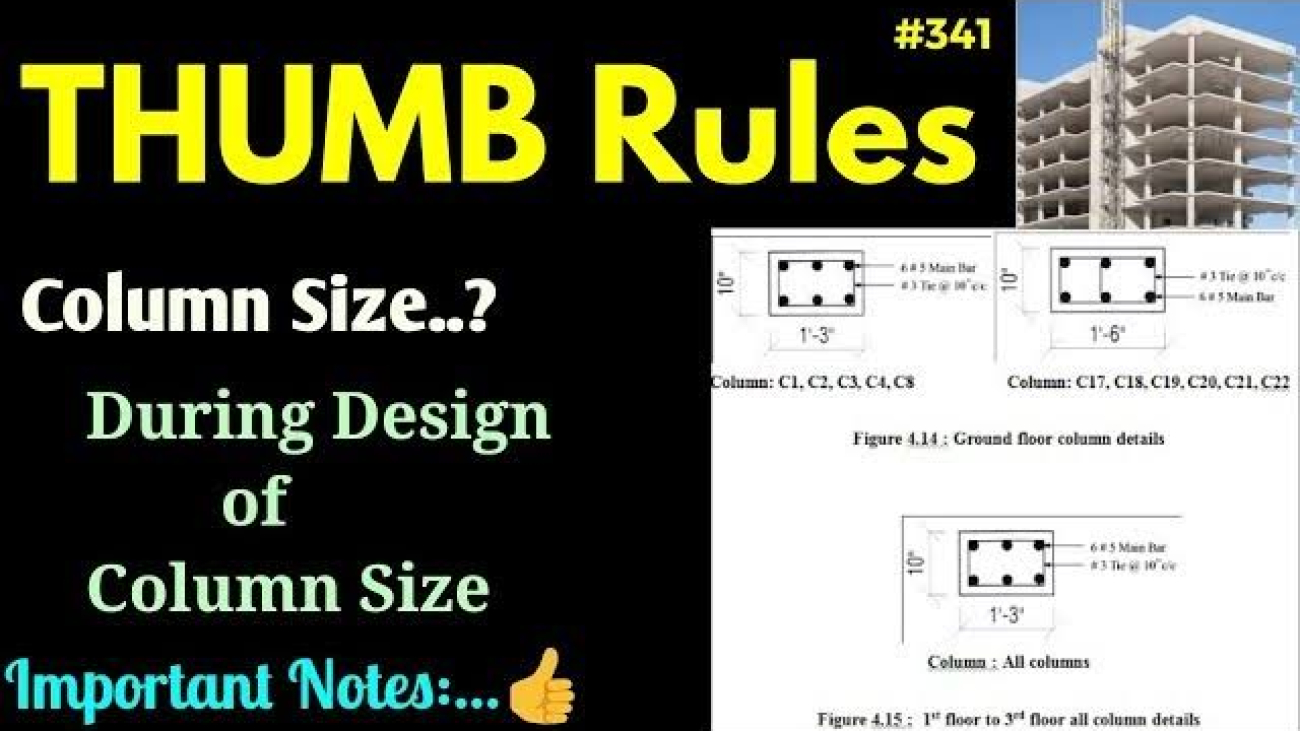
- Column Size:
- Single Storey: Minimum column size is 9” x 9” (230 mm x 230 mm) using M20 grade concrete. However, this can vary based on the load and structural requirements.
- 2 to 3 Storeys: Increase column size to 12” x 9” (300 mm x 230 mm) or 12” x 12” (300 mm x 300 mm).
- 4 to 5 Storeys: Minimum column size is 15” x 12” (375 mm x 300 mm) or 15” x 15” (375 mm x 375 mm).
- 6 to 10 Storeys: Column size can be 18” x 18” (450 mm x 450 mm) or larger, depending on load calculations.
- Steel Reinforcement:
- Single Storey: Use 4 bars of 12 mm diameter (Fe500 steel).
- 2 to 3 Storeys: Use 6 bars of 12 mm diameter or 4 bars of 16 mm diameter.
- 4 to 5 Storeys: Use 8 bars of 16 mm diameter.
- 6 to 10 Storeys: Use 10 to 12 bars of 20 mm or 25 mm diameter.
- Steel Calculation (Thumb Rule):
- For Residential Buildings: 1% to 2% of the cross-sectional area of the column.
- For Commercial Buildings: 2% to 3% of the cross-sectional area of the column.
Example Calculation:
For a 5-storey building with a 15” x 15” (375 mm x 375 mm) column:
- Area of Column: 375 mm x 375 mm = 140625 mm²
- Steel Requirement (2% of column area for residential building):
- Steel area = 0.02 x 140625 mm² = 2812.5 mm²
- Using 16 mm diameter bars (area = 201 mm² per bar):
- Number of bars required = 2812.5 mm² / 201 mm² = 14 bars (rounded up for practical design)
Important Considerations:
- Load Calculations:
- Dead Load: Weight of the structure itself.
- Live Load: Occupancy loads.
- Wind Load: Depending on the height of the building.
- Seismic Load: Based on the seismic zone.
- Soil Bearing Capacity:
- Type D soil typically has a bearing capacity around 100-200 kN/m². Ensure that the foundation design accommodates this to prevent excessive settlement.
- Concrete Grade:
- M20 or higher grade for residential buildings.
- M25 or higher for commercial buildings.
- Safety Factors:
- Include appropriate safety factors as per local building codes and standards.
- Building Codes:
- Follow the local building codes and standards (such as ACI318 and IS 456 etc.) for detailed and accurate design.
Final Note:
These thumb rules provide a quick reference, but detailed structural analysis and design should be performed by a qualified structural engineer using relevant design codes and standards, especially considering the specifics of load distribution, soil properties, and building use.